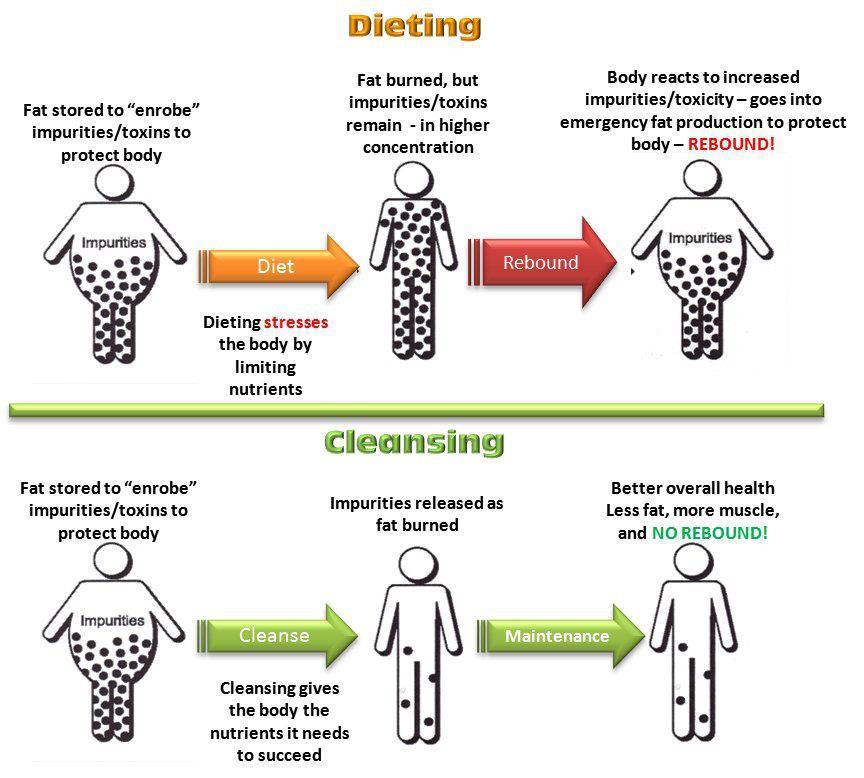
Introduction to Weight Loss Success
The secret to losing weight is staying full, satiated, and satisfied while eliminating (yes, pooping) regularly. No one likes the feeling of stomach emptiness or the sensation of starving or deprivation while trying to lose weight, so it is important to feel full by eating foods that are full of bulky fiber. This bulky fiber also helps sweep the intestinal tract to keep elimination regular. Regular elimination helps clean the body of impurities encapsulated by fat cells and helps reduce the size of fat cells.
Fiber is filling. Fiber is flushing. Sustainable weight loss happens when the body is clean and healthy.
It is estimated that nearly 20% of the population is constipated. Chronic constipation is a common problem that can be reversed and prevented in most cases. Ideally you will move your bowels at least once a day. Optimally you will move your bowels after each meal. Constipation is largely due to lack of insoluble fiber in the daily diet.
Click: The Constipation Crisis
Soluble & Insoluble Fiber
Dr. Garth Davis, weight-loss surgeon, has said that 97% of Americans are fiber deficient. Fiber deficiency comes from eating too many fiberless foods, too many highly processed foods stripped of fiber, and not enough fiber-rich whole foods.
There are two kinds of fiber in food. Both usually come packaged together in the same whole foods and both are important to feeling full and increasing elimination.
1. Soluble fiber attracts water and turns to gel during digestion. This slows digestion and keeps you feeling full longer. Soluble fiber is found in oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, and some fruits and vegetables. Because of its gel-like nature, soluble fiber collects food, sugar, fats, and cholesterol in the small intestines and carries them through and out the gastro-intestinal tract.
Prebiotics are indigestible food ingredients that stimulate the growth and maintenance of beneficial gut microbiota. Prebiotics are food for your gut flora, those living organisms that contribute to health and well being. Prebiotics are classified as soluble fiber. These being inulin and oligofructose, along with fructooligosaccharides (FOS), galactooligosaccharides (GOS), and other oligosaccharides. Pectin, too, appears to have some prebiotic potential, but inulin and oligofructose are the big ones. All of these can be obtained by eating several servings of vegetables and fruits each day.
2. Insoluble fiber is found in foods such as wheat bran, vegetables, and whole grains. Fiber, along with adequate water intake, adds bulk to the stool and moves quickly and relatively easily through your digestive tract and helps it function properly. A high-fiber diet may also help reduce the risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Insoluble fiber is found in high, whole carbohydrate foods and is not a component of protein or fat. Fiber has no calories so the more you eat has zero impact on your caloric intake. Eating 200 calories of food high in fiber is going to benefit you in multiple ways compared to eating 200 calories of food low in fiber.
Click: Know Your Complex, Simple, and Refined Carbs
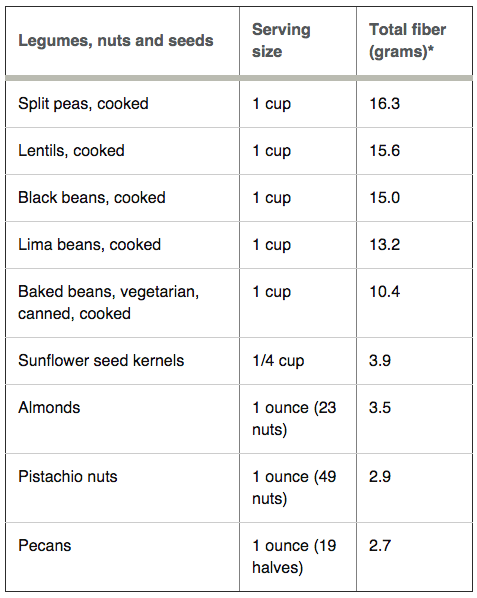
High Fiber Foods
Women should try to eat at least 21 to 25 grams of fiber a day, while men should aim for 30 to 38 grams a day.
Build your meals around high fiber whole plant foods in the charts below: whole fruits, whole vegetables, whole grains, and whole legumes. Keep skins on potatoes, apples, cucumbers and the like (buy organic in these cases if/when possible).
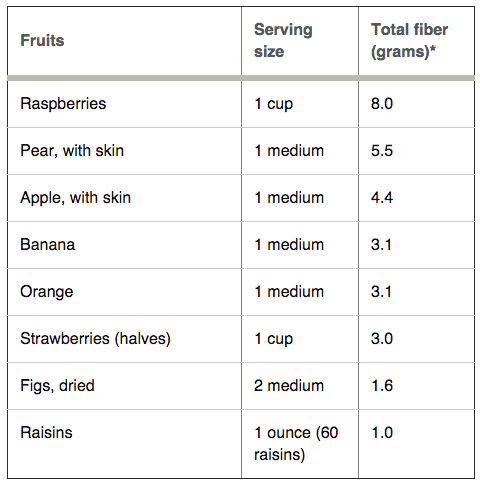
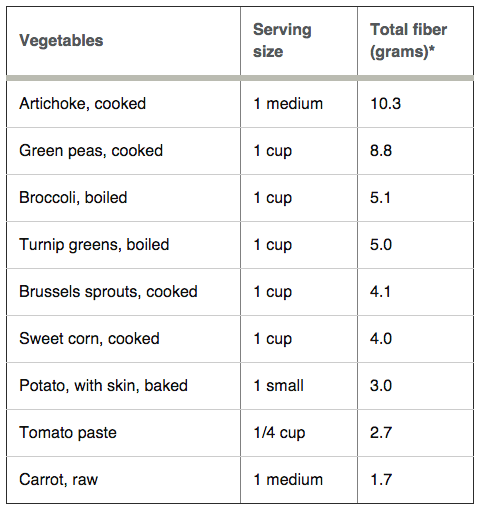
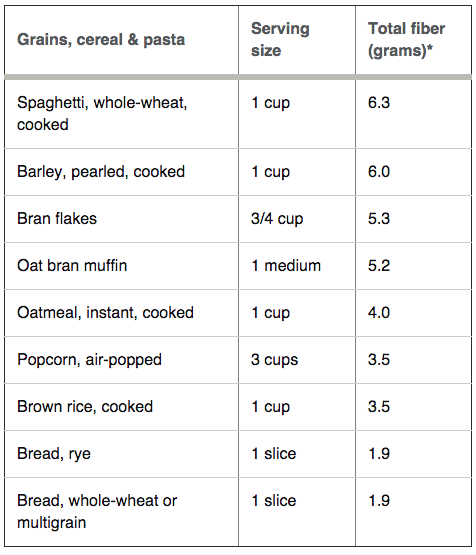

Low Fiber Foods
Any foods comprised of refined starches (flour) or refined sugar are foods low in fiber. Eliminate or minimize these foods.
• White bread
• White rice
• White pasta
• Crackers
• Refined hot cereals, such as Cream of Wheat, or cold cereals with less than 1 gram of fiber per serving
• Pancakes or waffles made from white refined flour
• Most canned or well-cooked vegetables and fruits without skins or seeds
• Fruit and vegetable juice with little or no pulp, fruit-flavored drinks, and flavored waters
• Tofu (tempeh is a higher fiber choice since it is made with the whole soy bean)
Refined carbohydrate starches are best avoided: flour, crackers, cookies, cakes, pies, muffins, most breads, corn flakes, crusts, couscous, cream of wheat or rice, crisped rice, de-germed cornmeal, enriched macaroni or spaghetti, most boxed cereals, white grits, pretzels, puffed rice or wheat, white breads, white rice, alcohol, soda, and any other naturally or artificially sweetened drinks.
The grains used for these refined products have been stripped of their best parts. White rice, white bread, and white flour are empty calories. Refined grains contain only the endosperm and lose up to 80 percent of their nutrients after the bran and germ are removed.
If you desire higher fiber bread and crackers, look for the brands below.
Sprouted grain breads, tortillas, and bagels to look for in the freezer section:
• Ezekiel bread
If crackers are desired, choose:
• Wasa – select non-GMO varieties
• Mary’s Gone Crackers
The best grain products have 5 grams of fiber or more per serving. If you’re up for a little more math, learn about Dr. Michael Greger’s 5:1 fiber rule HERE.
No Fiber Foods
Beef, pork, poultry, and fish (aka meat) are all zero-fiber foods. Milk, yogurt, butter, all types of cheese and other dairy products don’t contain fiber. You also won’t get fiber from eggs. In other words, animal-based foods are free of insoluble fiber.
Meat is muscle which is comprised of muscle fibers, but this is not soluble or insoluble fiber. This is meat fiber comprised of mostly protein.
Meat, dairy, and eggs have too much protein and dietary cholesterol and absolutely no fiber. The human body with its very long intestinal tract requires insoluble fiber to push food through the passage. True carnivores (cats, wolves, birds of prey) have very short intestinal tracts in comparison to humans and do not need plant fiber to move their bowels.
If you are not comfortably moving your bowels at least once a day, you are not getting enough dietary fiber. The solution is not to chug some fiber powder in fruit juice, but to cut back or eliminate fiberless meat, dairy, and eggs and increase whole fiber-rich fruit, veggies, grains, legumes, and tubers (root vegetables).
Bonus: Naturally Low Fat Foods
If you really want to up your weight loss progress, choose foods that are naturally high in fiber and low in fat.
High-fat whole plant foods to minimize or avoid:
• Avocados
• Coconut
• Nuts & Seeds (including nut butters)
Follow the link below to learn why all oils need to be avoided and how to cook & bake without oils. Salad dressings made with oil and margarine also need to be avoided for successful weight loss and the reversal of other lipid based diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Click: 6 Health-Preserving Reasons to Stop Consuming Oil
High Fiber, Low Fat Recipes & Resources
• Happy Herbivore cookbooks & website recipes
• Forks Over Knives cookbooks & website recipes
• PlantPure Nation & website recipes
• The Campbell Plan cookbook & website recipes
• Better Than Vegan cookbook
• The China Study Cookbook & website recipes
• Straight Up Food recipe blog
• Physicians Committee For Responsible Medicine cookbook & website recipes
• Dr. John McDougall cookbook & website recipes
• Dr. Joel Kahn book
• Dr. Michael Klaper website
• Dr. Michael Greger website
• Dr. Pam Popper website
Next Steps for Maximum Wellness
ONE: Use the free Getting Started on a Low Fat, Whole Food, Plant-Based Diet document.
TWO: Read the Protein Report.
THREE: Increase whole fiber foods and decrease low fiber & fiber-less foods.
With these resources, you’ll be well on your way to achieving your ideal weight and optimal health! Remember, you need to be healthy first to sustainably lose weight and keep it off. Rapid weight loss is exciting but done unsustainably without long-term health in mind will eventually backfire either by regaining the lost weight or decreased wellness or both. A sign of optimal health and balance is no longer struggling to lose excess weight.


{ 0 comments… add one now }